Superficial vein thrombosis (SVT) typically resolves within weeks and poses minimal risk. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT), however, can be dangerous. A DVT clot can break loose and travel to the lungs, potentially causing a life-threatening pulmonary embolism.
What Causes Blood Clots?
Blood clots in the legs can develop when blood flow slows or becomes restricted. Several key factors may increase the likelihood of clot formation:
- Limited Movement: Extended periods of sitting or lying down, such as during long flights or recovery after surgery, can slow blood circulation.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy and medications like birth control can alter the blood’s clotting properties.
- Health Conditions: Diseases such as cancer or heart disease may heighten clotting risks.
- Physical Trauma: Injuries or surgeries that damage blood vessels can trigger clot development.
- Lifestyle Impacts: Smoking and obesity significantly contribute to clotting disorders.
What are the Symptoms of a Blood Clot?
The symptoms of a blood clot can vary based on its location and severity:
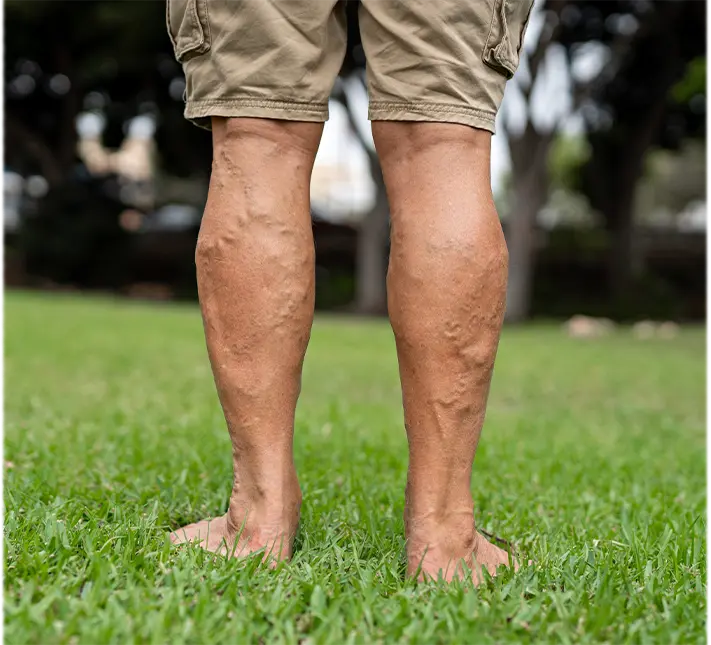
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT):
- Swelling, usually in one leg.
- Pain or tenderness, often starting in the calf.
- Skin discoloration or warmth over the affected vein.
Superficial vein thrombosis (SVT):
- Redness and inflammation near the surface of the skin.
- Tenderness or pain in the affected vein.
- A firm, cord-like feeling along the vein.
If you suspect a blood clot, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly, especially for DVT, as it can lead to severe complications.

What Are the Treatments for DVT and SVT?
Treatment for blood clots varies depending on the type and severity, with approaches tailored to specific medical needs, such as the clot’s location, size, and any associated complications. Common approaches include:
Medications:
- Blood thinners to prevent new clots and stop existing ones from growing
- Clot-dissolving drugs for severe cases
Compression Therapy:
- Specialized stockings to improve blood flow
- Reduce swelling and support circulation
Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Regular movement Leg elevation during rest
Surgical Interventions:
- Thrombectomy (clot removal)
- Vena cava filter placement in rare, complex cases
How to Prevent Blood Clots
To reduce the risk of developing blood clots, consider these preventive measures to help improve circulation and lower the chances of clot formation, especially if you are at higher risk due to certain lifestyle factors or medical conditions:
• Stay active and avoid sitting or standing still for long periods.
• Maintain a healthy weight and avoid smoking.
• Follow your doctor’s advice after surgery or during pregnancy.
• Wear compression stockings if recommended.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment of blood clots can improve outcomes. If you experience symptoms of DVT or SVT, talk to a vein specialist about the best treatment options for you.
What Our Patients Have to Say

IAC Accredited Vascular Testing
We are proud to be distinguished as an IAC Accredited Vascular Testing Facility. The Vein Institute adheres to the strictest national guidelines for vascular testing, demonstrating a commitment to the highest quality patient care.

