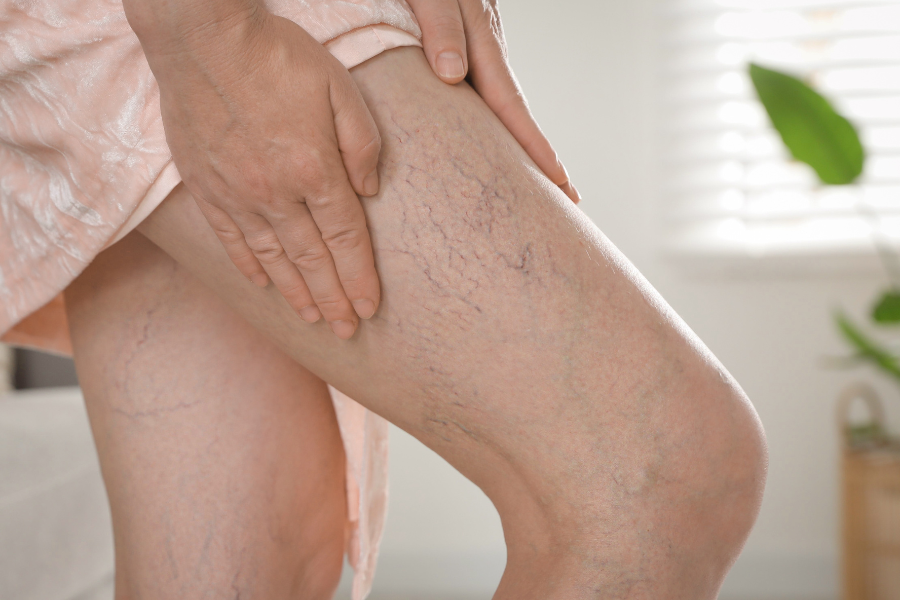
Sclerotherapy is the primary, if not only, treatment for getting rid of spider and reticular veins. But like any medical procedure, it does come with potential side effects. One of those is hyperpigmentation of the skin on a patient’s legs.
What is hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation is a discoloration of the skin, usually a brownish color and splotchy in appearance. It occurs in 9-30% of patients, depending on the chemical makeup of the sclerosing agent and the patient. Hyperpigmentation is more familiar with dark-skinned patients or patients with very dark hair. The good news is that post-sclerotherapy hyperpigmentation is usually temporary, fading within six months. More severe cases can last up to a year, and in a minimal number of patients, about one percent, hyperpigmentation can be permanent.
Tips to Minimize the Potential for Hyperpigmentation
- Choose your vein specialist carefully.
Look for a physician who has completed a fellowship in a specialty with advanced training in venous disorders as recognized by the American Board of Medical Specialties (ABMS) and has sought certification by the American Board of Phlebology. The latter demonstrates advanced knowledge and dedication to the treatment of venous disorders. - Follow instructions.
After your treatment, follow your physician’s instructions for wearing your compression hose entirely. Maintaining Proper compression is critical because it minimizes the blood reentering the injected area, improves venous blood flow, and thus, decreases the incidence of post-sclerotherapy hyperpigmentation and telangiectatic matting. - Don’t take supplemental vitamins with iron.
Do not take supplemental iron or multivitamins that contain iron. It has been shown that hyperpigmentation is frequently related to the iron in a patient’s blood.
If you have spider veins, reticular veins, or varicose veins, call 904.901.6575 (VEIN) or complete our online form to request a consultation.
Frequently Asked Questions

IAC Accredited Vascular Testing
We are proud to be distinguished as an IAC Accredited Vascular Testing Facility. The Vein Institute adheres to the strictest national guidelines for vascular testing, demonstrating a commitment to the highest quality patient care.
Known as CVI, chronic venous insufficiency, is a medical condition in which the veins are unable to pump enough oxygen-poor blood back to the heart. It’s caused by damaged blood valves and often occurs after deep vein thrombosis or phlebitis. While women make up the majority of CVI sufferers, it’s also common among men who […]
Education is key to maintaining lifelong vascular health at The Vein Institute of Jacksonville. One of the most common questions we hear from patients is whether genetics can predict their risk for developing Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI). Let’s explore the connection between family history, vein disease, and the steps to stay ahead of symptoms. What […]
Chronic venous insufficiency is a condition that affects millions of people around the world, and yet it often goes unrecognized. In this article, we’ll discuss what chronic venous insufficiency is, what its symptoms are, and why it’s important to seek medical help if you think you may be suffering from it. Let’s get started! Introduction […]